Alzheimer’s disease research is at the forefront of scientific discovery, driven by innovative minds like neuroscientist Beth Stevens. Her groundbreaking work with microglial cells—the brain’s immune system—has reshaped our understanding of how these cells impact neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s. By exploring the processes of synaptic pruning and neuroinflammation, Stevens is unlocking potential new Alzheimer’s treatments that could revolutionize patient care. With approximately 7 million Americans living with Alzheimer’s today, her insights are crucial for early diagnosis and effective management of this complex condition. The collaboration between institutions like Boston Children’s Hospital and the Broad Institute highlights a vital commitment to combating the rising tide of dementia as our population ages.
Exploring the complexities of dementia, research on Alzheimer’s disease offers significant insights into the mechanisms behind this challenging health crisis. By focusing on the role of immune cells in the brain, particularly microglia, researchers such as Beth Stevens are revealing how these critical components interact with neuronal health. This line of inquiry not only sheds light on the underlying causes of neurodegenerative disorders but also paves the way for promising therapeutic interventions. Addressing the growing prevalence of memory-related illnesses as the population ages necessitates a deep dive into these biological processes, ensuring that emerging treatments will tackle the root problems efficiently. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of cognitive decline, the importance of foundational research becomes ever clearer in shaping future care strategies.
Understanding the Role of Microglial Cells in Alzheimer’s Disease
Microglial cells serve as the brain’s immune response, constantly monitoring for signs of damage or disease. In the context of Alzheimer’s disease, these cells play a pivotal role in the complex processes of synaptic pruning—removing unnecessary or dysfunctional synapses to maintain cognitive function. However, recent research highlights that aberrant microglial activity can contribute to the progression of Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases by improperly pruning healthy synapses. This dysfunction not only disrupts neural communication but may also exacerbate the neurodegenerative processes associated with Alzheimer’s.
Beth Stevens’ innovative research has shed light on how microglial cells can sometimes become overly aggressive, leading to detrimental effects on brain health. The Stevens Lab at Boston Children’s Hospital posits that targeting these cells could provide new avenues for therapies. By understanding how microglial cells function within the brain’s immune system, scientists can develop strategies that harness their protective roles against Alzheimer’s disease, while curbing their harmful effects. This dual approach could revolutionize treatments, making early intervention in Alzheimer’s disease more feasible.
Innovative Treatments Emerging from Alzheimer’s Research
The transformation in our understanding of microglial cells has significant implications for developing new Alzheimer’s treatments. As researchers like Beth Stevens continue to uncover the intricate relationship between immune responses in the brain and neurodegenerative processes, the potential for innovative therapeutic strategies becomes apparent. For instance, targeted therapies aimed at modulating microglial activity can potentially restore balance in synaptic pruning, alleviating the symptoms of diseases such as Alzheimer’s.
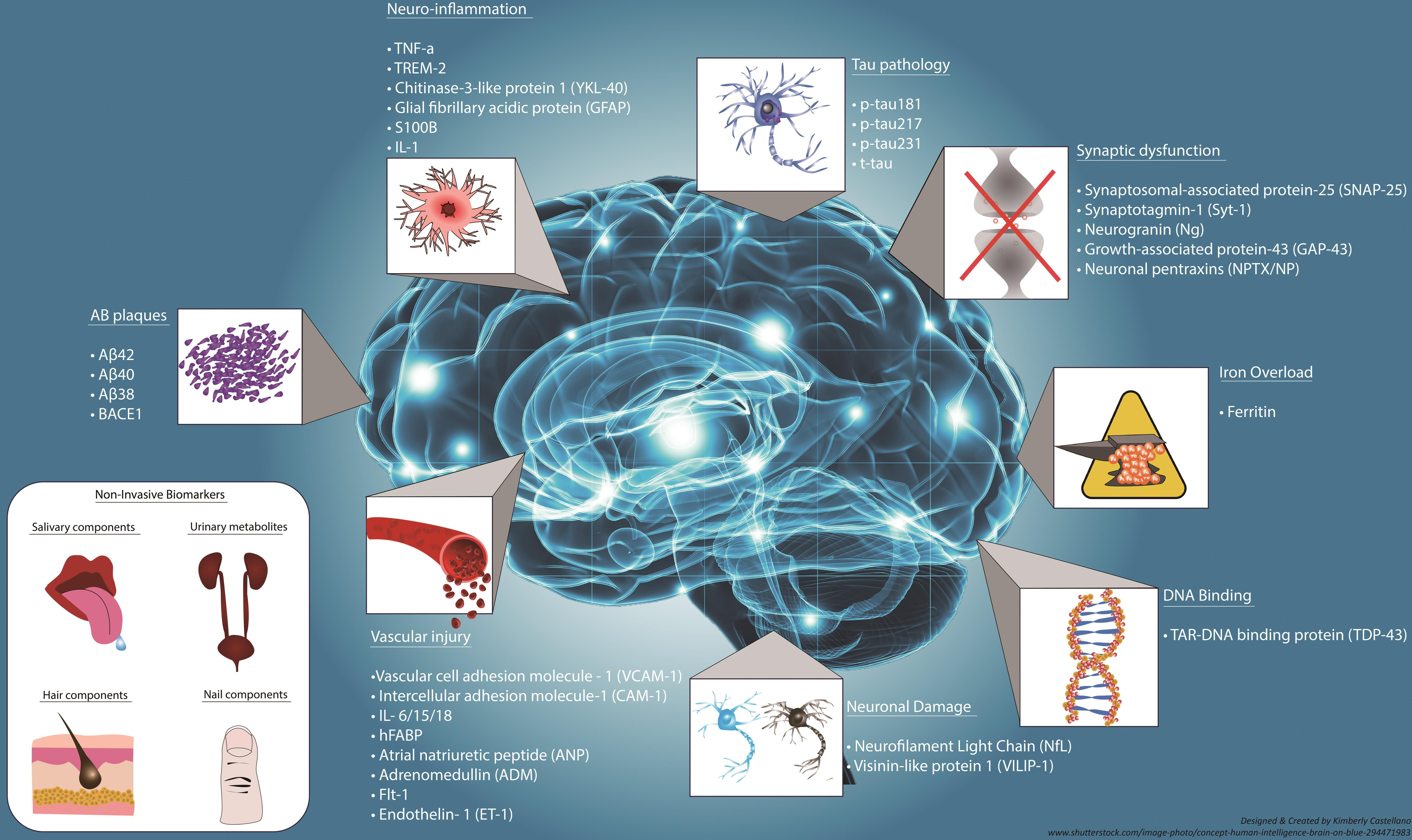
Additionally, the emergence of biomarkers linked to microglial functioning offers the promise of earlier diagnosis. By identifying specific markers of neuroinflammation or abnormal pruning patterns, clinicians can detect Alzheimer’s disease much earlier than traditional methods allow. Proactive measures resulting from such early detection could lead to personalized treatment plans that effectively slow disease progression and improve the quality of life for millions.
The Future of Alzheimer’s Disease Research and Treatment
As the global population ages, the urgency for advancements in Alzheimer’s disease research has peaked. Current estimates indicate that by 2050, the number of individuals affected by Alzheimer’s in the U.S. alone could surpass 14 million. Hence, funding for Alzheimer’s research is critical. Institutions like the National Institutes of Health (NIH) are pivotal in providing the necessary resources for innovative studies, such as those conducted by the Stevens Lab. Continuous investment in this sector will ensure that neuroscientists can explore new avenues of treatment and prevention.
Furthermore, collaborations between research institutions, healthcare providers, and pharmaceutical companies are essential in translating laboratory discoveries into practical applications. By fostering a synergistic approach, the field can accelerate the development of novel treatments and interventions that target the underlying mechanisms of Alzheimer’s disease. Public awareness and support for Alzheimer’s research will also play a crucial role in shaping a future where effective treatments are available to tackle this devastating disease.
Beth Stevens: A Pioneer in Neuroimmune Research
Recognized for her groundbreaking contributions to neuroimmunology, Beth Stevens has become a leading figure in Alzheimer’s research. Her work fundamentally challenges previous assumptions about microglial cells, emphasizing their role not only in disease pathology but also in normal brain function. This paradigm shift is essential as it opens new avenues for research into how the immune system can be leveraged to combat neurodegenerative diseases. Stevens’ commitment to following the science has led to transformative ideas that have the potential to alter the trajectory of Alzheimer’s research.
Stevens’ accolades, including being named a MacArthur ‘genius,’ underscore her impact in the scientific community. Through her dedication, she exemplifies the importance of scientific curiosity and foundational research in the quest to unravel the complexities of Alzheimer’s disease. By understanding microglial behavior and their interactions within the brain’s immune systems, Stevens paves the way for innovative therapies that could one day not only treat Alzheimer’s but also enhance overall brain health.
The Importance of Federal Funding in Alzheimer’s Research
Federal funding has played a critical role in advancing Alzheimer’s research, particularly in studies involving microglial cells. Grants from agencies like the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have supported essential projects that explore the intersection of neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. These funds enable scientists like Beth Stevens to conduct transformative research that deepens our understanding of the brain’s immune responses, leading to potential breakthroughs in treatment strategies.
Without sustained federal investment, the pace of discovery in Alzheimer’s research could significantly lag. The complexities of neurodegenerative diseases require robust funding to support exploratory studies, clinical trials, and the development of new technologies. As the burden of Alzheimer’s disease continues to grow, collaborative efforts to secure funding are essential to ensure that groundbreaking research into its causes, progression, and treatments continues to thrive.
Leveraging Basic Science to Combat Neurodegenerative Diseases
Basic science is the cornerstone of medical breakthroughs, especially in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s. Understanding fundamental mechanisms—like microglial function—provides the foundation needed to develop effective treatments. Beth Stevens emphasizes the necessity of curiosity-driven research to uncover unexpected pathways and relationships among brain cells.
By researching the basic properties of microglial cells, scientists can better understand their dual roles in maintaining brain health and in contributing to Alzheimer’s pathology. This knowledge not only aids in creating targeted therapies but also informs the development of preventive strategies that can preserve cognitive function as the population ages. Sustained support for basic science is vital in uncovering the solutions necessary to combat diseases like Alzheimer’s effectively.
Identifying Biomarkers for Early Alzheimer’s Detection
The identification of biomarkers is a promising frontier in Alzheimer’s research, enabling earlier diagnosis and intervention. Beth Stevens’ research has led to potential biomarkers linked to microglial activity, which can signal the onset of Alzheimer’s before significant symptoms emerge. Early detection through biomarker assessment could revolutionize how we approach treatment, allowing patients to receive timely therapies that may slow disease progression.
Moreover, these biomarkers can facilitate the development of personalized medicine approaches in Alzheimer’s care. By understanding the unique pathophysiological processes at play in each patient, healthcare providers can tailor interventions to effectively target the individual’s underlying disease mechanisms. This approach not only enhances patient outcomes but also reduces the broader societal costs associated with Alzheimer’s disease care.
The Interplay Between Neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s Disease
Neuroinflammation is a critical factor in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease, often mediated by microglial cells. Understanding how these immune cells react to pathological changes in the brain helps researchers unravel the complexities of Alzheimer’s. Stevens’ lab has pioneered studies exploring the underlying causes and implications of neuroinflammation, revealing how chronic activation of microglia can lead to neuronal damage and cognitive decline.
Addressing neuroinflammation through therapeutic means presents a promising strategy for combating Alzheimer’s disease. By leveraging knowledge gained from recent research, developing anti-inflammatory therapies that specifically target microglial dysfunction could help restore balance within the brain’s immune environment. This therapeutic avenue is supported by growing evidence linking neuroinflammation to the pathology of various neurodegenerative diseases.
Advancing Genetic Research in Alzheimer’s Disease
In addition to exploring the role of microglia, advancing genetic research is vital in understanding Alzheimer’s disease. Genetic factors influence an individual’s susceptibility to neurodegenerative diseases, and studies conducted in Stevens’ lab are elucidating how specific genetic variations impact microglial function and Alzheimer’s pathology. By identifying these genetic markers, researchers can discern patterns that contribute to the risk and progression of the disease.
Moreover, understanding the genetic basis of Alzheimer’s allows for the development of targeted therapies that address these specific vulnerabilities. This approach not only enhances the efficacy of treatment but also supports the personalization of therapeutic interventions based on an individual’s genetic makeup. As genetic research continues to Fortschritt, its alignment with microglial studies could yield powerful insights into combating Alzheimer’s disease.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do microglial cells relate to Alzheimer’s disease research?
Microglial cells are integral to Alzheimer’s disease research as they function as the brain’s immune system, helping to clear away damaged cells and maintain brain health. Recent studies reveal that abnormal microglial activity, particularly in how they prune synapses, can contribute to neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer’s.
What role does Beth Stevens play in Alzheimer’s treatments?
Beth Stevens, a prominent researcher in Alzheimer’s disease, has pioneered studies on microglial cells, demonstrating their influence on synaptic pruning. Her research aims to develop new treatment options for Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases by identifying the mechanisms behind microglial dysfunction.
What advancements in Alzheimer’s disease research have emerged from studying neurodegenerative diseases?
Research in neurodegenerative diseases, particularly around microglial cells, has led to significant advancements in understanding Alzheimer’s disease pathology. By exploring how these immune cells interact with neural networks, scientists hope to identify biomarkers and innovative treatments for Alzheimer’s.
Why are microglial cells a focal point in current Alzheimer’s disease research?
Microglial cells have become a focal point in Alzheimer’s disease research because they are crucial for maintaining brain homeostasis and play a significant role in synaptic development. Abnormal functioning of these cells has been linked to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s, making them critical targets for new therapeutic strategies.
What impact does Beth Stevens’ research have on the future of Alzheimer’s disease treatment?
Beth Stevens’ research is expected to have a profound impact on the future of Alzheimer’s disease treatment. By improving our understanding of how microglial cells contribute to neurodegeneration, her work can lead to the development of new medications and strategies aimed at mitigating the effects of Alzheimer’s.
How can understanding brain immune systems aid in developing Alzheimer’s treatments?
Understanding the brain immune system, particularly the role of microglial cells, can aid in developing Alzheimer’s treatments by revealing how immune responses contribute to neurodegeneration. This knowledge allows researchers to create targeted therapies that restore healthy immune function in the brain.
What are some of the potential biomarkers being explored in Alzheimer’s disease research?
In Alzheimer’s disease research, potential biomarkers being explored include those related to microglial cell activity and synaptic pruning processes. Identifying these biomarkers may enable earlier diagnosis and intervention, providing better outcomes for individuals with Alzheimer’s.
How does curiosity-driven research contribute to advancements in Alzheimer’s disease understanding?
Curiosity-driven research fosters innovation in Alzheimer’s disease understanding by allowing scientists to explore unconventional ideas and complexities of brain function. This approach has led to groundbreaking discoveries about microglial cells and their role in Alzheimer’s, paving the way for future treatments.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Research Focus | Beth Stevens’ research focuses on microglial cells, which are the immune cells of the brain and play a crucial role in synaptic pruning. |
| Impact on Alzheimer’s Disease | Abnormal pruning by microglia is linked to Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases, highlighting the importance of proper immune function in the brain. |
| Potential for New Treatments | Stevens’ findings are paving the way for new medications and biomarkers that could lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment. |
| Funding and Support | Much of the foundational research has relied on federal funding, particularly from the National Institutes of Health. |
| Future Outlook | With the aging U.S. population, the number of Alzheimer’s cases is expected to double by 2050, leading to increased healthcare costs. |
Summary
Alzheimer’s disease research is at a pivotal point, driven by groundbreaking studies like those by Beth Stevens, who is transforming our understanding of how microglial cells affect brain health. By illuminating the detrimental effects of these immune cells on synaptic pruning, her work opens the door to new treatment strategies for the millions affected by Alzheimer’s. The integration of basic scientific inquiry and clinical application remains essential in addressing the rising challenges posed by Alzheimer’s, particularly as the American population ages. With continued support and innovative research efforts, there is hope for better outcomes in managing this devastating disease.





