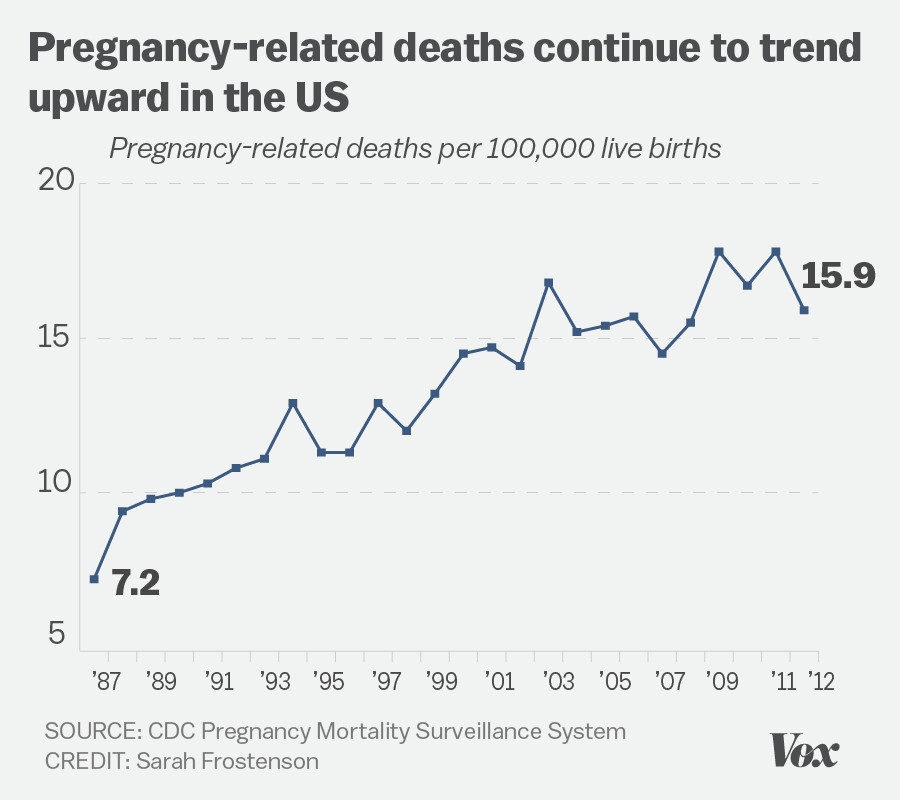
U.S. pregnancy-related deaths have reached alarming rates, consistently marking the nation as a leader in maternal mortality compared to other high-income countries. Recent studies indicate that over 80% of these tragic outcomes are preventable, yet the pregnancy mortality rate continues to rise, highlighting systemic issues within pregnancy health care. Disparities in maternal health outcomes reveal a concerning trend, with significant racial disparities in maternal mortality rates observed across various demographics. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women face mortality rates nearly four times higher than their white counterparts. As we delve into the underlying causes of this crisis, it becomes evident that improving prenatal and postpartum care, alongside addressing racial disparities in maternal health, is crucial for safeguarding the lives of mothers across the United States.
The increase in preventable deaths during or shortly after childbirth in the United States signals a pressing public health challenge that demands immediate attention. Maternal mortality, a broader term that encompasses deaths occurring during pregnancy and up to a year postpartum, affects many families and communities. The persistent rise in pregnancy mortality highlights the urgent need for improved maternity care systems and equitable health policies. Racial inequities complicate this issue further, as certain groups experience disproportionately high rates of complications and death. Addressing these factors through comprehensive reforms in pregnancy health care and policy interventions is essential for ensuring safer pregnancies for all women.
Understanding U.S. Pregnancy-Related Deaths
The United States has seen a troubling rise in pregnancy-related deaths, casting a spotlight on the shortcomings of its maternal health care system. According to recent studies, over 80% of these deaths are preventable. This alarming statistic highlights an urgent need for improved pregnancy health care to help mitigate risks associated with childbirth. Factors contributing to these high mortality rates include lack of access to adequate prenatal care and insufficient support during the postpartum period, reinforcing the notion that systemic changes are crucial for addressing this public health crisis.
The rise in pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. can be attributed to various interlinked factors. Racial disparities in maternal health significantly compound this issue, with American Indian and Alaska Native women facing the highest mortality rates compared to their white counterparts. This stark contrast illustrates the need to develop targeted interventions that address not just general maternal health care issues, but specifically the structural inequities faced by different racial and ethnic groups. Without such focused strategies, the U.S. will continue to lag behind other high-income countries in reducing pregnancy mortality.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main contributors to the increasing U.S. pregnancy-related deaths?
The increase in U.S. pregnancy-related deaths can be attributed to various factors including a fragmented healthcare system, inequitable policies, and systemic biases impacting maternal health. A notable contributor is the rise of chronic conditions such as cardiovascular disease among pregnant individuals, exacerbating pregnancy mortality rates.
How does the U.S. pregnancy mortality rate compare with other high-income countries?
The U.S. has the highest pregnancy mortality rate among high-income countries, with a troubling rise in maternal deaths over recent years. This discrepancy is largely due to various social and healthcare challenges that the U.S. faces, which impede effective pregnancy healthcare and postpartum care.
What role do racial disparities play in maternal mortality in the U.S.?
Racial disparities have a significant impact on maternal mortality in the U.S., with American Indian and Alaska Native women facing the highest rates of pregnancy-related deaths, nearly four times greater than white women. This highlights persistent inequities within the healthcare system, necessitating urgent attention and targeted policy changes.
Why is postpartum care critical in reducing pregnancy-related mortality?
Postpartum care is vital as nearly a third of pregnancy-related deaths occur between 42 days and one year post-pregnancy. Improving postpartum healthcare systems to provide continuous monitoring and support can significantly reduce these late maternal deaths and enhance overall maternal health.
What can be done to improve pregnancy health care in the U.S. and reduce mortality rates?
To enhance pregnancy health care and mitigate mortality rates, investments in public health infrastructure are essential. This includes funding innovative care solutions during pregnancy and the postpartum period, addressing state-level disparities, and prioritizing maternal health in policy discussions to ensure better access to quality care.
How have recent data collection improvements affected our understanding of maternal mortality?
Recent improvements, such as the implementation of the pregnancy checkbox on death certificates, have allowed for better tracking of maternal mortality since 2018. This advancement provides clearer insights into the causes of pregnancy-related deaths, informing targeted interventions to improve pregnancy health care.
What is the current status of U.S. pregnancy-related deaths compared to 2018?
As of 2022, U.S. pregnancy-related deaths remained alarmingly higher than in 2018, reflecting an ongoing crisis in maternal health. The data indicates that not only is the mortality rate increasing, but it also reveals concerning trends related to age, chronic health conditions, and racial disparities in maternal mortality.
What is the significance of the rise in cardiovascular disease as the leading cause of pregnancy-related death?
The rise of cardiovascular disease as the leading cause of pregnancy-related death signifies a shift in maternal health trends. This highlights the need for heightened awareness and intervention strategies focusing on managing chronic health conditions such as hypertension, which are affecting younger pregnant individuals.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| U.S. Pregnancy-Related Deaths | The U.S. continues to have the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, with a rate of 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2022. |
| Preventability | More than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable. |
| Race and Ethnicity Disparities | Significant disparities exist in maternal mortality based on race. American Indian/Alaska Native women face the highest rate, followed by Black and then White women. |
| Leading Causes of Death | Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of pregnancy-related death, with increased rates in women aged 25 to 39. |
| Late Maternal Deaths | Late maternal deaths (42 days to 1 year post-pregnancy) account for nearly one-third of all maternal deaths. |
| Need for Improved Care | Better prenatal and extended postpartum care is critical. Changes in healthcare policies and investments are necessary. |
Summary
U.S. pregnancy-related deaths are a significant public health concern, with the nation experiencing the highest rates among high-income countries. A recent study highlights alarming trends in maternal mortality, demonstrating that the U.S. needs substantial improvements in healthcare delivery and policy to address these disparities and ensure the safety of mothers across all demographics. Prompt action and investment in maternal health infrastructure are essential to reverse this troubling trajectory and reduce preventable deaths.





