Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked considerable debate among health experts and nutritionists alike. Many individuals experience intense sugar cravings, which can lead to what some refer to as sugar addiction. While the health risks of sugar consumption are becoming better understood, distinguishing between a dependency on sugar and true addiction, like that seen with alcohol or nicotine, is complex. Excess sugar can contribute to compulsive eating behaviors and withdrawal-like symptoms, highlighting the significant impact of sugar on our physiological and psychological well-being. As we navigate sugar consumption recommendations, understanding our relationship with sugar is crucial in promoting healthier habits.
The allure of sweet treats raises a fundamental question about their potential addiction-like qualities in our daily lives. Defining this phenomenon as a dependency on refined carbohydrates may shed light on the frequent cravings many individuals experience. Known for its ability to enhance flavor and satisfaction, sugar also poses health risks when consumed in excess, creating a fine line between enjoyment and overindulgence. Considering guidelines for sugar intake is pivotal, as reducing excessive sugar consumption can have positive effects on overall health. The discussion around the addictive nature of sweeteners may help us better understand how our dietary choices influence our well-being.
Understanding Sugar Addiction: Is Sugar Addictive?
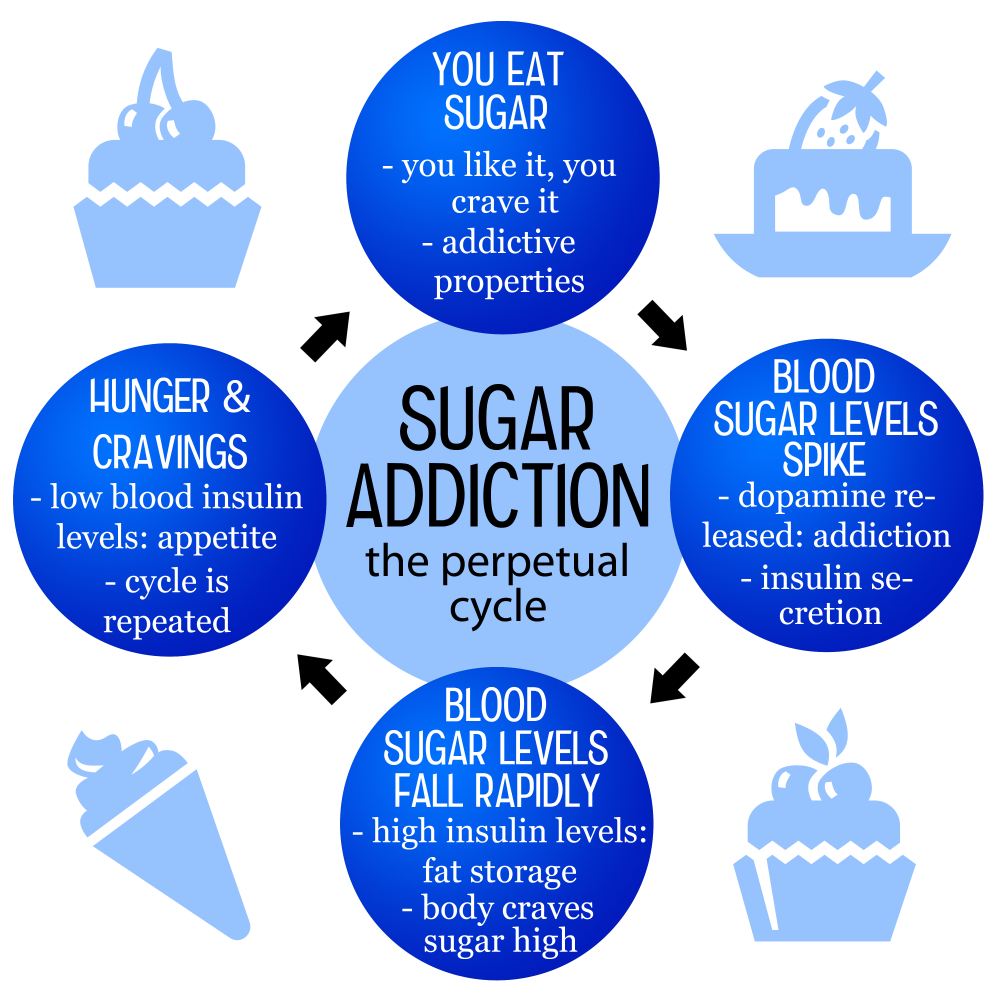
The debate around sugar addiction has gained traction in recent years as more studies surface highlighting its impact on our cravings and eating behaviors. While it’s essential to differentiate between sugar and substances like alcohol or nicotine, the cravings that can stem from excessive sugar consumption are undeniably strong. Many individuals report withdrawal-like symptoms when they significantly reduce or eliminate sugar from their diet, including irritability and mood swings. This mirrors aspects of traditional addiction, where the compulsion to consume a substance becomes overwhelming.
However, health experts, including nutrition scientists from institutions such as Harvard, assert that sugar addiction is a more complex issue. Unlike illicit drugs, some natural sugars found in fruits and vegetables are vital for our health. Thus, it’s crucial to evaluate sugar based on the amount consumed rather than classifying it purely as an addictive substance. Understanding the nuances of sugar cravings can lead to healthier consumption habits, ensuring people enjoy sweetness without overwhelming potential health risks.
Health Risks of Excessive Sugar Consumption
With the current average of nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar consumed daily by Americans, the health risks associated with excessive sugar intake can be alarming. High sugar consumption is linked to various health issues, including obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and even certain cancers. Furthermore, the impact of sugar on our bodies extends beyond physical health; it also plays a significant role in mental health. Excessive sugar can lead to mood swings, anxiety, and depression, many people find themselves trapped in a cycle of cravings that perpetuate unhealthy eating behaviors.
In response to these alarming health statistics, organizations like the American Heart Association recommend limiting added sugar intake to no more than 6 teaspoons for women and 9 teaspoons for men each day. Educational resources, such as food labels, can empower consumers to make more informed decisions about their sugar consumption. By focusing on moderation and understanding the health risks associated with excessive sugar, individuals can create balanced diets that integrate natural sources of sweetness without compromising their overall health.
The Connection Between Sugar Cravings and Mental Health
The relationship between sugar cravings and mental health is a crucial area of consideration when discussing the effects of sugar in our lives. Many people reach for sugary treats during stressful times, seeking comfort or a temporary mood boost. This psychological attachment to sugar can contribute to a cycle of overconsumption, where individuals rely on sweets to feel better, thus exacerbating their cravings over time. As sugary foods trigger the release of neurotransmitters like dopamine, they create a short-lived feeling of pleasure that can become addictive.
It’s important to recognize this cycle and find healthier coping mechanisms for stress and emotional distress. Developing mindfulness practices or alternative habits, such as exercise or engaging in hobbies, can reduce reliance on sugary foods. Acknowledging the psychological effects of sugar on our cravings allows individuals to take proactive steps in managing their intake, ultimately enhancing their overall mental and emotional well-being.
The Role of Ultra-Processed Foods in Sugar Consumption
The prevalence of ultra-processed foods in our diets is a significant contributor to excessive sugar consumption. Many of these convenience foods are laden with added sugars, unhealthy fats, and other ingredients designed to enhance flavor and increase palatability. As a result, they lead to strong cravings and habitual consumption, making it challenging for individuals to moderate their sugar intake. The accessibility and marketing of these products can make them irresistible, further complicating the relationship between diet and health.
Reducing the consumption of ultra-processed foods can significantly decrease daily sugar intake, paving the way for healthier dietary habits. Focusing on whole, minimally processed foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can naturally satisfy sweetness cravings without the adverse effects associated with excessive sugar consumption. Encouraging mindful eating practices and meal planning can help individuals make better food choices, ultimately reducing the risks associated with high sugar intake.
Making Sense of Sugar Consumption Recommendations
Understanding and adhering to sugar consumption recommendations is vital for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. The American Heart Association suggests limiting added sugars to specific daily amounts: no more than 6 teaspoons for women and 9 teaspoons for men. These recommendations aim to mitigate health risks associated with excessive sugar intake while allowing room for natural sugars found in fruits, vegetables, and dairy products, which are essential for a balanced diet.
Being aware of these guidelines encourages consumers to read food labels, assess their dietary habits, and make necessary adjustments to lower their sugar intake. Gradually reducing added sugars rather than attempting to cut them out entirely can help avoid withdrawal symptoms and foster a sustainable approach to healthier eating. By being proactive and informed, individuals can enjoy the sweetness in their diets without compromising their health.
Mindful Strategies for Reducing Sugar Cravings
Implementing mindful strategies to reduce sugar cravings can be instrumental in achieving a balanced diet. For instance, developing awareness around binge eating tendencies and identifying emotional triggers can help individuals make healthier choices. Many experts suggest keeping a food diary to track sugar intake and cravings, which can illuminate patterns that may need addressing. Additionally, practicing moderation, rather than total elimination of sugar, can promote a more positive relationship with food.
Exploring alternative sweeteners or healthier snack options can also satisfy cravings while minimizing added sugar consumption. Incorporating a variety of whole foods into meals, such as fruits, nuts, and seeds, can provide natural sweetness and necessary nutrients. By focusing on these mindful strategies, individuals can effectively manage their cravings and improve their overall dietary habits.
The Importance of Education in Sugar Consumption Awareness
Education plays a pivotal role in sugar consumption awareness. By informing the public about the health risks associated with high sugar intake and the presence of added sugars in common processed foods, individuals can make more informed choices about their diets. Awareness initiatives can include community workshops, online resources, and school programs that focus on nutrition education, empowering people to understand food labels and make healthier eating decisions.
Moreover, initiatives promoting awareness about the recommended sugar intake can help families become conscious of their dietary habits. Encouraging discussions about sugar and healthy alternatives among family members can create a supportive environment for improved dietary choices. Ultimately, education is key to combating the issues surrounding excessive sugar consumption and fostering a healthier society.
Transforming Sugar Habits for Better Health
Transforming sugar habits is crucial for anyone looking to improve their health. Starting with small changes, like gradually reducing the amount of added sugar in daily meals, can significantly benefit long-term health outcomes. For example, replacing sugar-laden beverages with water or herbal tea can decrease daily sugar intake while still satisfying thirst. Similarly, opting for natural sweeteners or enjoying whole fruits can provide sweetness without excessive calories.
Establishing a support network can also aid in transforming sugar habits. Engaging with friends, family, or online communities focused on healthy eating can help maintain motivation and accountability. By sharing resources, recipes, and success stories, individuals can foster an encouraging environment that promotes healthier choices and sustains lifestyle changes over time.
Navigating Social Situations with Sugar
Social situations often pose challenges when it comes to managing sugar intake. Events like parties, celebrations, and dining out can expose individuals to higher levels of temptation due to sugary foods and beverages. Acknowledging this and preparing strategies to navigate these situations is essential for maintaining healthy habits. Informing friends and family about dietary preferences can also help create an inclusive environment that accommodates individual choices.
Bringing a healthy dish to social gatherings can not only ensure that there’s something suitable to enjoy but can also inspire others to consider healthier options. Additionally, practicing mindful eating in social settings, such as savoring flavors and engaging in conversation, can help minimize the likelihood of mindless overconsumption. By being proactive and prepared, individuals can effectively navigate social situations while maintaining control over their sugar intake.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like alcohol or drugs?
Sugar is debated among experts as potentially having addictive qualities, but it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or drugs. While it can create cravings and compulsive behaviors, the withdrawal symptoms are generally milder compared to true addictive substances.
What are the health risks of sugar addiction?
Excessive sugar consumption can lead to health risks including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. These risks are exacerbated by compulsive eating behaviors associated with high-sugar diets, which can result from sugar addiction. Moderation is key to maintaining health.
How do sugar cravings relate to sugar addiction?
Sugar cravings can stem from habitual consumption of sugary foods, leading to a cycle that resembles sugar addiction. These cravings can trigger a desire for more sugar, reinforcing the cycle of consumption. Understanding this relationship can help in managing cravings.
What impact does excessive sugar consumption have on health?
Excessive sugar consumption increases the risk of various health problems, including weight gain, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular diseases. It may also lead to psychological issues such as anxiety or mood swings related to sugar dependency.
What are the current sugar consumption recommendations?
The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar to no more than 9 teaspoons per day for men and 6 teaspoons for women. Children should consume even less, maintaining a balanced diet while being mindful of sugar intake.
Can reducing sugar intake help with sugar addiction?
Yes, gradually reducing sugar intake can help manage sugar addiction. Sudden elimination may trigger withdrawal-like symptoms, so a gradual decrease allows the body to adjust and decreases cravings over time.
Why are processed foods associated with sugar addiction?
Processed foods often contain high levels of added sugar, unhealthy fats, and sodium, making them highly palatable and addictive. These foods can lead to habitual consumption and increased sugar cravings, reinforcing unhealthy eating patterns.
What role does sugar play in our diets?
While sugar can contribute to cravings and has addictive qualities, it is also a necessary part of a balanced diet when consumed in moderation. Natural sugars found in fruits and vegetables provide essential nutrients and energy.
Is it possible to have a healthy relationship with sugar?
Yes, it is possible to maintain a healthy relationship with sugar by consuming it in moderation, being mindful of added sugars in processed foods, and focusing on a balanced diet rich in whole foods.
How can I combat sugar addiction effectively?
Combating sugar addiction involves being aware of sugar intake, reading food labels, gradually reducing sugary foods, and incorporating healthier alternatives while ensuring your diet remains balanced and satisfying.
| Key Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Sugar Addiction Debate | Sugar is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine, but it can lead to cravings and compulsive eating. |
| Physical and Psychological Effects | Withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, and anxiety can occur when sugar intake is reduced. |
| Ultra-Processed Foods | Foods high in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium can increase cravings and habitual consumption. |
| Recommended Sugar Intake | The American Heart Association recommends no more than 9 teaspoons for men and 6 teaspoons for women. |
| Gradual Reduction Suggested | Reducing sugar intake gradually is recommended rather than going cold turkey to avoid backlash. |
| Need for Some Sugar | Some sugar is necessary for flavor and pleasure in our diets; complete elimination isn’t feasible. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This topic has sparked substantial debate among researchers and nutrition experts. Although sugar can stimulate cravings and compulsive behaviors akin to addictive substances, it doesn’t meet the clinical criteria for addiction. Understanding the effects of sugar consumption, especially in the context of ultra-processed foods, is vital. While some withdrawal symptoms may be experienced when reducing sugar intake, moderation rather than elimination is key to enjoying a healthy diet.





